Specific Defense
http://www.ehow.com/facts_6752456_functions-suppressor-cell_.html
http://www.biooncology.com/images/therapeutic-targets/b-cell-lg.jpg
http://www.roche.com/pages/downloads/photosel/061106/original/p004.jpg
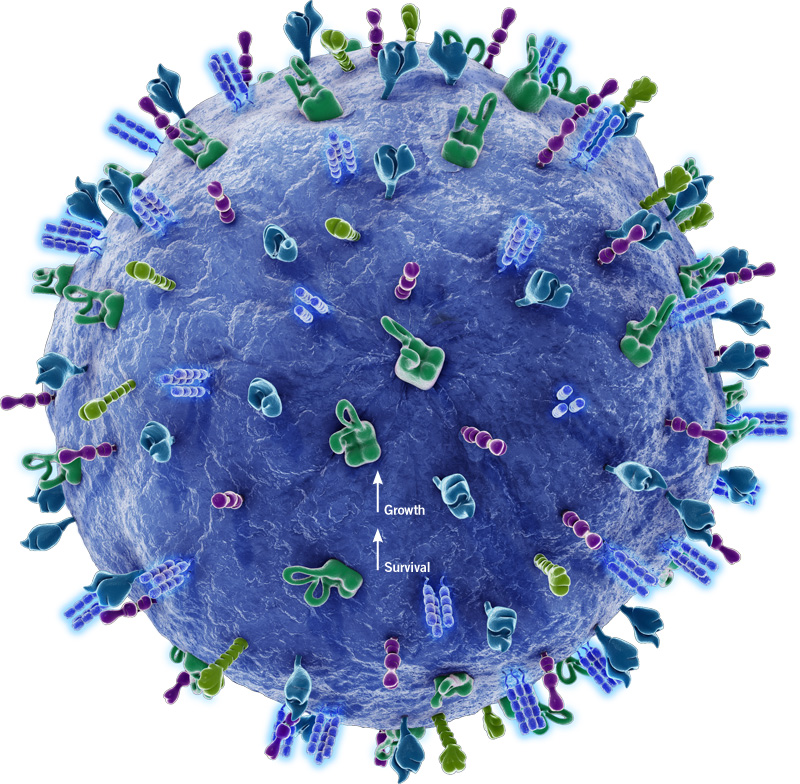
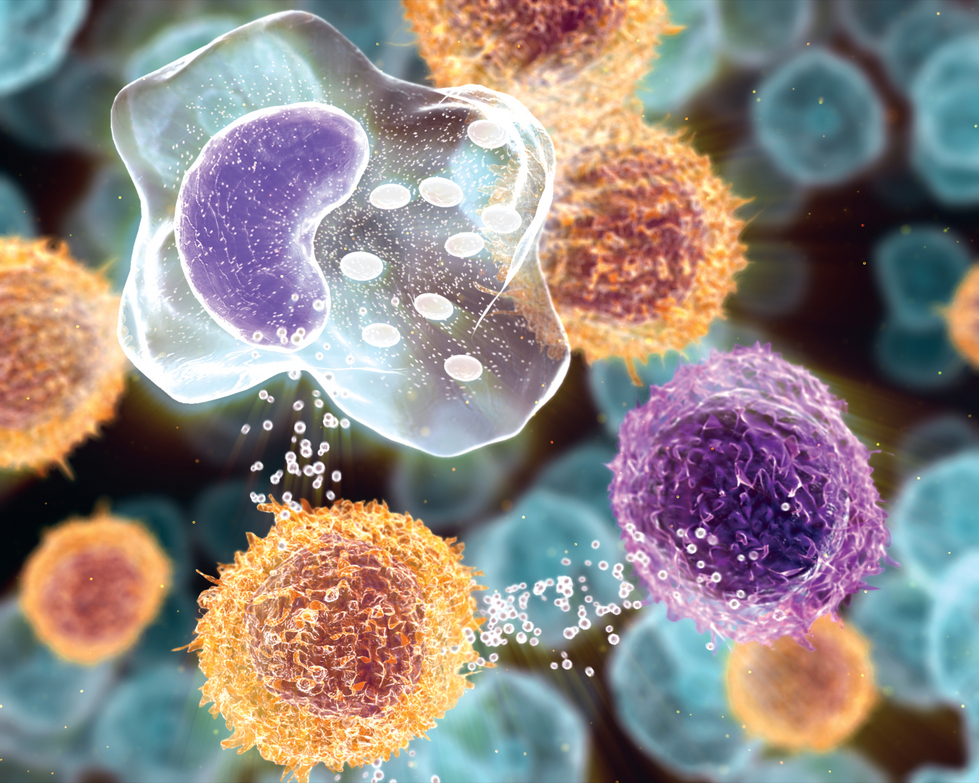
The specific defense is consists of lymphocytes- a type of white blood cell. They are produced in the bone marrow and some migrate to other parts of the lymphatic system, such as the spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils and adenoids. There is also a transportation system of lymph vessels for extra storage and delivery of lymphocytes, and also to flush out dead cells. There are two types of lymphocytes:
B lymphocytes produce antibodies against a specific antigen in a humoral response.
T lymphocytes fight pathogens directly which is called cell-mediated response. Both are produced in the bone marrow and circulate in the blood. They recognize different specific antigens (anything that triggers an immune response)
On the surface of every cell is a potential antigen. The immune system recognizes the cells with foreign cells (cells from outside the body), and attacks those cells.
Antibodies are proteins that either attach the invaders or mark them for killing. They have the ability to bind to only one particular antigen. They neutralize antigens by binding to them, signaling them for phagocytes to devour.
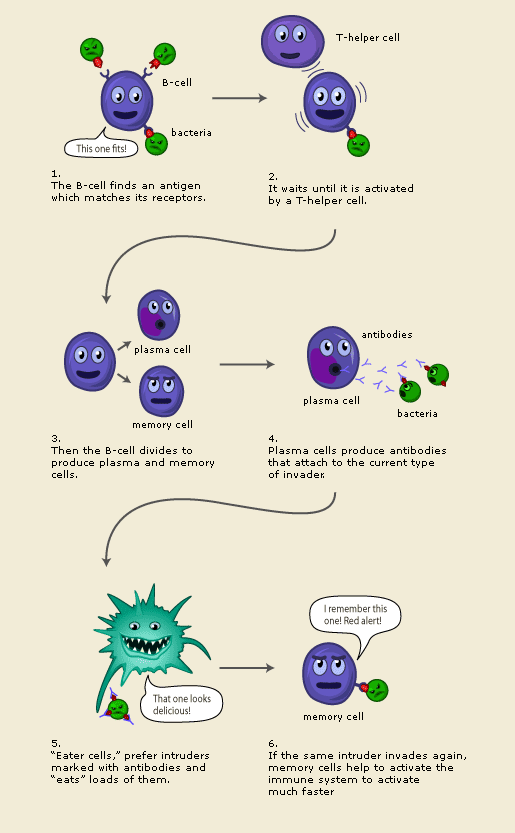
B lymphocytes (B cells) can differentiate into plasma cells and memory cells. Plasma cells are produced to fight antigens immediately (called primary immune response) and have short life spams. Memory cells fight the same antigens, but they have a much longer life spam, usually for a life time. There are memory cells for every viral infection you have been sick with and every vaccine you've gotten. Immunological memory is the capacity of the immune system to generate a secondary immune response. This is why you can not get chicken pox twice; once you've had it, you're body has the B memory cells that prevents you from getting it again. In other words, you are immune to it.
B lymphocytes produce antibodies against a specific antigen in a humoral response.
T lymphocytes fight pathogens directly which is called cell-mediated response. Both are produced in the bone marrow and circulate in the blood. They recognize different specific antigens (anything that triggers an immune response)
On the surface of every cell is a potential antigen. The immune system recognizes the cells with foreign cells (cells from outside the body), and attacks those cells.
Antibodies are proteins that either attach the invaders or mark them for killing. They have the ability to bind to only one particular antigen. They neutralize antigens by binding to them, signaling them for phagocytes to devour.
B lymphocytes (B cells) can differentiate into plasma cells and memory cells. Plasma cells are produced to fight antigens immediately (called primary immune response) and have short life spams. Memory cells fight the same antigens, but they have a much longer life spam, usually for a life time. There are memory cells for every viral infection you have been sick with and every vaccine you've gotten. Immunological memory is the capacity of the immune system to generate a secondary immune response. This is why you can not get chicken pox twice; once you've had it, you're body has the B memory cells that prevents you from getting it again. In other words, you are immune to it.
http://www.nobelprize.org/educational/medicine/immunity//immune-detail.html
Background: Antibodies sending messages to cells
http://iahealth.net/wp-content/uploads/2009/09/antibodies.bmp
http://iahealth.net/wp-content/uploads/2009/09/antibodies.bmp